Podio Calculation Fields - Comprehensive V8 Migration Guide (v4.3 > v11.1.277.13)
This document provides a consolidated, production‑ready migration guide for Podio Calculation fields as the JavaScript runtime upgrades from Google V8 v4.3 to v11.1. It covers performance improvements, newly available language features, breaking changes with fixes, deterministic patterns, Podio‑specific behaviors, and a pragmatic rollout plan.
Examples are JavaScript‑only and tailored to Calculation fields.
In this article:
- Overview and context
- Why the new V8 is faster
- New JavaScript features you can use
- Backward‑Incompatible changes and fixes
- Migration principles and best practices
- Deterministic patterns (Seeded PRNG, Sorting, Dates, Text)
- Testing and validation strategy
- Rollout and operational plan
- References
- Appendices: Quick recipes
Overview & Context
Podio Calculation field execute JavaScript to compute Number, Date, or Text outputs directly in app items. The engine upgrade spans a decade of ECMAScript evolution (ES2015 > ES2020+). This guide explains what changes, how to modernize safely, and how to validate behavior for predictable results in Podio.
Why the new V8 is faster
Modern V8 uses a multi‑tier pipeline that materially improves startup and steady‑state performance in real workloads:
- Ignition (interpreter) + TurboFan (optimizing compiler): faster warm‑up, higher‑quality machine code.
- Sparkplug baseline compiler: lightweight baseline tier that boosts throughput for small scripts typical of Calculation fields.
- Orinoco garbage collection: parallel/incremental GC reduces latency and pause times under load.
- Ongoing micro‑optimizations (e.g., numeric paths) and modern inline caching lower property access overhead. Net result: calculations run more efficiently, with fewer pauses and more predictable timing.
New JavaScript features you can use
The upgrade enables a broad set of modern language features. Below are the most relevant for Calculation fields, with concise examples.
Optional chaining (?.) & Nullish coalescing (??)
Safely access nested tokens and apply correct defaults without clobbering valid falsy values.

Template literals & Arrow functions

Modern Array methods

BigInt (precise large integers)

RegExp enhancements (named groups, lookbehind, dotAll)

Intl API (date/number formatting)

Stable Array.prototype.sort (ES2019)

Backward‑Incompatible Changes & Fixes
Sorting is stable now — define tie‑breakers
Legacy code sometimes relied on unstable sort behavior for ties. Modern V8 guarantees stability; explicitly add secondary keys.

Math.random() behavior differs across engine versions
Do not depend on engine‑specific sequences. If reproducibility matters, use a seeded PRNG (see §6).
Date parsing & formatting nuances
ISO strings with ‘Z’ are UTC; date‑only strings are often interpreted as UTC midnight and then shifted into local time. Store ISO with an explicit offset or ‘Z’, and use Intl only for display.

Podio‑specific: refresh order is not guaranteed
Calculations can run concurrently; avoid chains that assume an order. Compute directly from raw inputs and eliminate circular dependencies.

Calculation output types are immutable
If a field switches from Number to Text (or Date), recreate the Calculation field to change its output type.
Migration principles and best practices
- Replace logical OR
||with nullish coalescing??for defaults. - Use optional chaining (?.) for nested references and method calls.
- Prefer map()/reduce()/filter() for array processing.
- Flatten multi‑step calculation chains; avoid refresh‑order assumptions.
- Confirm each Calculation field’s output type (Number/Date/Text) after changes.
- Test date parsing with explicit ISO and offsets; beware date‑only strings.
- Validate text with String.prototype.toWellFormed() before encoding/transmitting.
- Add explicit secondary keys in comparators; do not rely on unstable ties.
- Use a seeded PRNG for deterministic selection when necessary.
Deterministic Patterns (Seeded PRNG, Sorting, Dates, Text)
Seeded PRNG (predictable randomness)
A seeded PRNG generates the same sequence when initialized with the same seed. This is useful for reproducible selections and tests.

Deterministic sorting

Date precision & display

Unicode safety

Testing & Validation Strategy
- Create a sandbox app and copy representative items and relationships.
- Run side‑by‑side comparisons (old vs. new) on totals, sorts, and string outputs.
- Test dates across time zones (e.g., Europe/Sofia) and different ISO shapes (UTC ‘Z’, offset, date‑only).
- Stress test calculations with large related lists to observe stability and performance.
- Use deterministic seeds for PRNG logic to ensure reproducible results.
- Bulk refresh by safely touching the template to trigger recalculation across items.
Rollout & Operational Plan
- Phase 1 — Readiness: inventory calculations; classify by risk (sorting, randomness, dates).
- Phase 2 — Pilot: migrate a small, representative workspace; collect metrics and outputs.
- Phase 3 — Broad rollout: apply fixes (comparators, seeded PRNG, ISO dates), then roll out by app tier.
- Phase 4 — Post‑migration verification: run regression views; monitor calculation queues and latency.
- Backout — maintain a revert plan for templates if an unexpected output change is detected.
References
- V8 modern JavaScript overview (Ignition/TurboFan, ES2015+)
- Stable sort (ES2019)
- Math.random internals & improvements
- BigInt feature
- Intl.DateTimeFormat (MDN)
- String.prototype.toWellFormed (MDN)
- ECMAScript edition history
- Podio Calculations docs
- Podio calculation behavior (refresh order)
Appendices: Quick Recipes
Optional chaining + nullish

Comparator with tie‑breaker
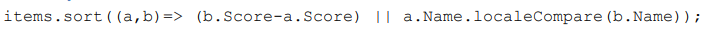
Deterministic selection (seeded)

Code Modernization Examples
Defaulting and Safe Arithmetic

Safe Nested Field Access

Compact Text Concatenation

Aggregation and Summation

Group Totals Using Object.groupBy

Locale-Aware Sorting

Date and Currency Formatting

Unicode Sanitization

In this article
- Overview & Context
- Why the new V8 is faster
- New JavaScript features you can use
- Backward‑Incompatible Changes & Fixes
- Migration principles and best practices
- Deterministic Patterns (Seeded PRNG, Sorting, Dates, Text)
- Testing & Validation Strategy
- Rollout & Operational Plan
- References
- Appendices: Quick Recipes